Selecting the right measuring tools is crucial for ensuring accuracy and efficiency in any project, whether it’s in construction, engineering, cooking, or any other field requiring precise measurements. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you make informed decisions:
1. Understand Your Measurement Needs
Before diving into the types of tools available, clarify what you need to measure. Consider:
- Dimension: Length, width, height, depth, or circumference.
- Units: Metric (millimeters, centimeters, meters) or Imperial (inches, feet).
- Precision: The degree of accuracy required (e.g., millimeters for engineering vs. centimeters for carpentry).
2. Types of Measuring Tools
Here’s a rundown of common measuring tools and their applications:
a. Rulers and Tape Measures
- Best for: General measurements of length and width.
- Materials: Plastic, wood, metal.
- Precision: Suitable for tasks needing moderate accuracy.
- Tip: Choose a tape measure with clear, easy-to-read markings.
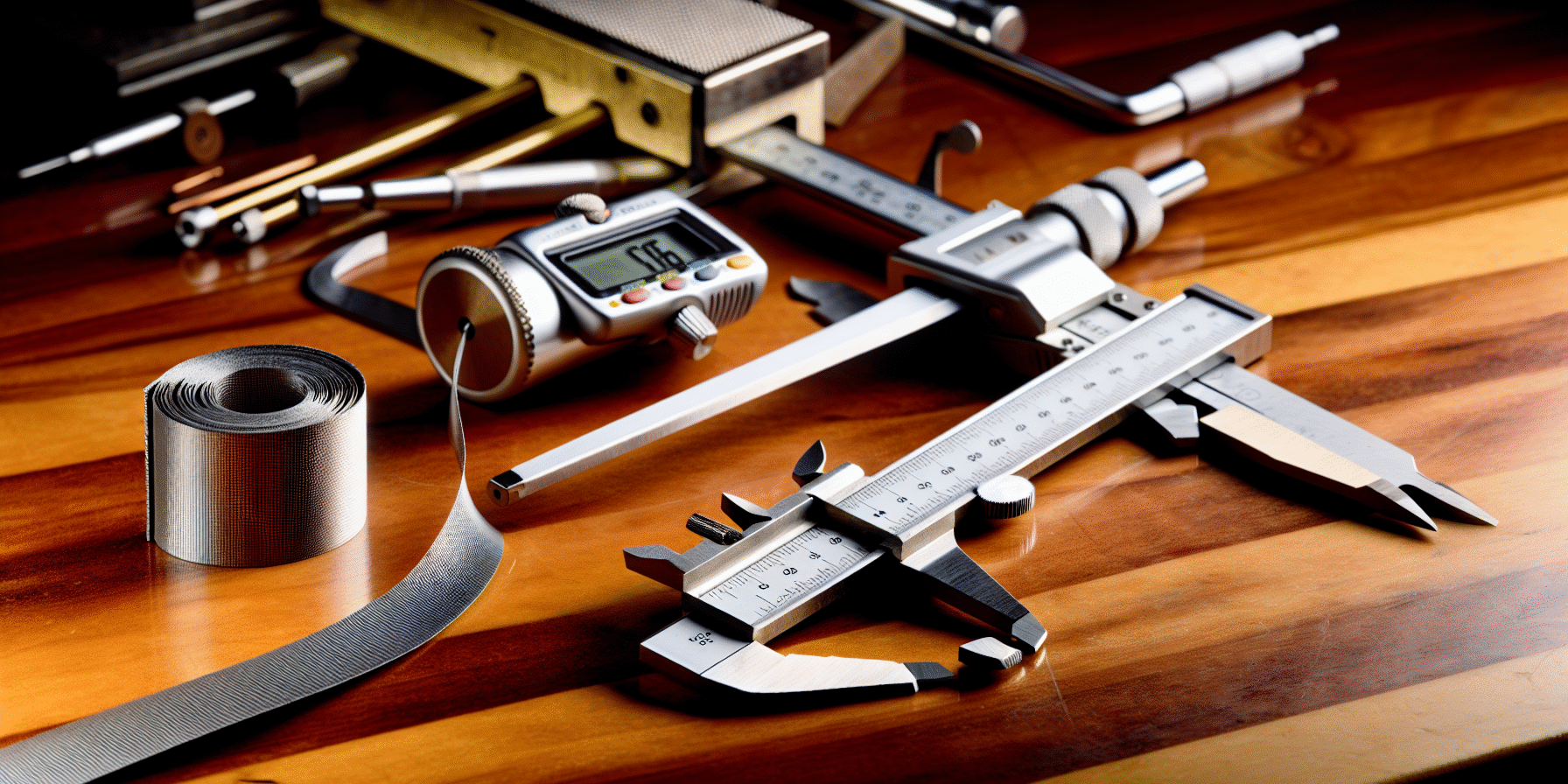
b. Calipers and Micrometers
- Best for: Measuring the thickness or diameter of small objects.
- Types: Vernier, digital, and dial calipers.
- Precision: High; can measure to the nearest 0.01 mm.
- Tip: Digital calipers are user-friendly and reduce human error.
c. Laser Measures
- Best for: Measuring distances in large spaces.
- Precision: High; accurate to within millimeters over long distances.
- Tip: Ideal for surveying, real estate, and large construction projects.
d. Protractors and Angle Finders
- Best for: Measuring angles.
- Types: Simple protractors, digital angle finders.
- Precision: Varies; digital versions provide higher accuracy.
- Tip: Use digital angle finders for tasks requiring precise angle measurements, like woodworking.
e. Scales and Balances
- Best for: Measuring weight.
- Types: Mechanical, digital.
- Precision: High, especially with digital scales.
- Tip: Ensure the scale is calibrated correctly for accurate readings.
3. Material and Build Quality
- Durability: Choose tools made from robust materials like stainless steel for longevity.
- Comfort: Ergonomically designed tools reduce fatigue and improve measurement consistency.
- Maintenance: Opt for tools that are easy to clean and maintain to ensure long-term accuracy.
4. Ease of Use
- Readability: Clear, large markings make measurements quicker and reduce errors.
- Features: Look for additional features such as backlighting on digital displays or lock mechanisms on tape measures.
- Portability: Consider the size and weight of the tool if you need to carry it around frequently.
5. Calibration and Accuracy
- Calibration: Regular calibration ensures your tools remain accurate. Some tools come with calibration certificates.
- Standards Compliance: Check if the tool complies with industry standards (e.g., ISO, NIST).
6. Cost and Budget
- Investment: High-quality tools may cost more but are usually worth the investment for their accuracy and durability.
- Comparison: Compare different brands and models to find the best value for your needs.
7. Brand and Reviews
- Reputation: Established brands often offer better reliability and support.
- Reviews: Read customer reviews and expert opinions to gauge the performance and reliability of the tool.
Conclusion
Choosing the right measuring tools involves understanding your specific needs, evaluating the types of tools available, considering build quality, ease of use, and ensuring regular calibration for accuracy. Investing time in selecting the right tools will pay off in the precision and efficiency of your work.
By following this guide, you can confidently select measuring tools that best suit your projects, ensuring accuracy and enhancing your overall productivity.